On January 2, 2020, the United States agency FDA (Food and Drug Administration) opened the new year with a ban.
American stores have thirty days to stop the sale of certain fruit and mint-flavoured vaping products.
Meanwhile in Canada, essentially all provinces and territories are also looking at making their own similar bans or having tighter regulations in 2020. The main reason?
To protect young people from getting access to these products.
So why is there concern around vaping, especially for youth? And what exactly is vaping anyway?
What is vaping?
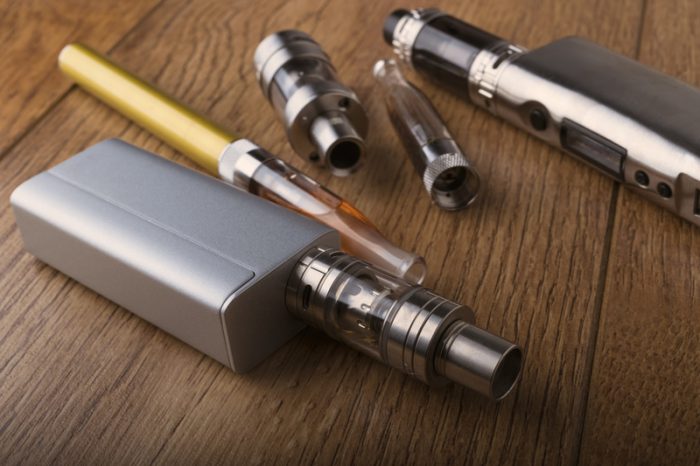

Vaping devices come in a variety of styles, but all work in similar ways. (© Hazem Mohamad - Dreamstime.com)
Vaping is the act inhaling and exhaling an aerosol that is made by a vaping device, such as an e-cigarette (electronic cigarette). An aerosol is a vapour that has solid particles or liquid droplets suspended inside of it.
How is the aerosol created?
Inside the battery-powered device, a liquid is heated until it becomes a vapour. This vapour is usually flavoured and also contains chemicals, such as nicotine.
What is nicotine?
In many countries around the world, cigarette packages must have clear warnings about the dangers of smoking. (Getty Embed)
For hundreds of years, some humans have inhaled and exhaled the smoke produced by burning tobacco leaves, using either pipes or cigarettes. And the key ingredient in smoking was nicotine—a stimulant that produced an energetic feeling.
But in the 20th century, more and more studies emerged to show that smoking was very harmful to people's health and could lead to certain cancers. By the 1980s, governments faced huge pressure to better regulate smoking. This included banning smoking in public places and buildings, and making cigarette companies put clear warnings on their packages.
How does vaping factor into this?
People have tried all sorts of things to try and quit smoking. Even this! (Getty Embed)
After learning of the dangers of cigarettes, many smokers were eager to quit their habit. But cigarettes — in particular, nicotine — are also highly addictive, making it extremely challenging to stop smoking.
Vaping first became popular in the early 2000s as possible way of helping people quit. Because vaping didn't burn anything, it released far fewer dangerous chemicals. The idea was that smokers could use vaping as a less harmful way to still get nicotine, while they worked on ultimately quitting altogether.
Did it work?
Yes and no. There are definitely examples of people who used vaping to eventually quit.
But vaping also became popular as a habit on its own. Because it didn't burn anything, vaping aerosol could come in all kinds of appealing flavours that cigarettes never could. In addition, whether from a cigarette or a vape, nicotine is still an addictive substance.
Why are bans happening now?
Fruit-flavoured vaping products like this are now banned in the United States. (Getty Embed)
When vaping first became popular, there was very limited research into how it affected the body. But now that the habit has been common for a while, alarming studies are showing that vaping has its own serious health concerns. These include lung disease and even deaths.
Another problem? The ability to make vapes that are fruit-flavoured means that many young people who might have avoided smoking due to the smell or taste could be more open to trying vaping.
What are the bans currently?
Both smoking and vaping are banned in many public places. (Getty Embed)
The short answer? If you're under 18 anywhere in Canada or the U.S. it is illegal to buy any vaping products. Also, all vaping is banned anywhere that smoking is already banned.
In the U.S., as we mentioned, there are now bans on fruit and mint flavoured vaping liquids.
Beyond that, it seems that both federal, provincial, and state governments will be spending 2020 making their own laws regulating vaping. These include restrictions on advertising and where vapes can be sold.
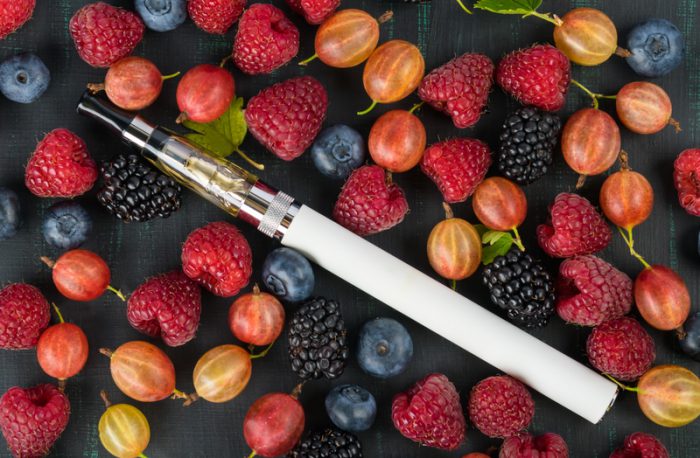 Fruit and mint-flavoured vaping products are facing bans across North America for the dangers they pose. (© Andrey Kurguzov - Dreamstime.com)
Fruit and mint-flavoured vaping products are facing bans across North America for the dangers they pose. (© Andrey Kurguzov - Dreamstime.com)









That’s great! Vaping and Smoking is Awful! 😎 😎 😎 😎 😎 😎 😎 😎
You bet.
I know that vaping and smoking are not good for you but banning it makes it impossible to get. I don’t think we should ban vaping and smoking ,we should just tell everyone how they are harmful for your body.
It would not be fair to ban smoking because other people like smoking. If people ban smoking other people will really not be happy. There could be protesting.